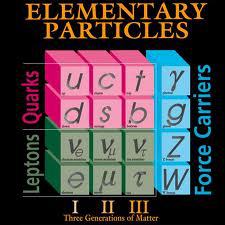
Physics - The Science of Matter and its Motion
Physics (the word comes from Ancient Greek: φύσις physis "nature") is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through the universe with related concepts such as energy and force.
In a more general way it is the analysis of nature, which is carried out in order to understand how the universe behaves.
Physics is considered of the oldest academic disciplines, perhaps the oldest as it includes astronomy.
In a more general way it is the analysis of nature, which is carried out in order to understand how the universe behaves.
Physics is considered of the oldest academic disciplines, perhaps the oldest as it includes astronomy.
Physics intersects with many areas of scientific research involving more than one science discipline such as biophysics and quantum chemistry, and the boundaries of physics are not rigidly defined.
New ideas in physics often explain the fundamental mechanisms of other sciences, while opening new avenues of research in areas such as mathematics and philosophy.
Physics uses concepts such as force and energy to uncover the mathematical principles on which the universe operates. It leads to discoveries and problem solving about how things work, by thinking logically and carefully whilst analysing experiments.
Physics uses concepts such as force and energy to uncover the mathematical principles on which the universe operates. It leads to discoveries and problem solving about how things work, by thinking logically and carefully whilst analysing experiments.
Advances in thermodynamics led to the development of industrialisation; and advances in mechanics inspired the development of calculus.
Physics also makes significant contributions through advances in new technologies that arise from theoretical breakthroughs. Noteworthy examples include advances in the understanding of electromagnetism or nuclear physics led directly to the development of new products which have dramatically transformed modern-day society, such as television, computers, domestic appliances, and nuclear energy.
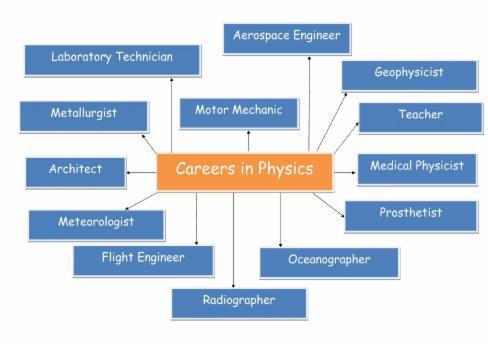
Physics can unite the world of words and numbers and give you the ability to present a clear and precise view in a discussion and the opportunity to enter either a career in science or anything involving numbers.
Examples include Engineering, Astrophysics, Teaching, Banking, Accountancy or Music and Sound Technology.
Physics also makes significant contributions through advances in new technologies that arise from theoretical breakthroughs. Noteworthy examples include advances in the understanding of electromagnetism or nuclear physics led directly to the development of new products which have dramatically transformed modern-day society, such as television, computers, domestic appliances, and nuclear energy.
Physics can unite the world of words and numbers and give you the ability to present a clear and precise view in a discussion and the opportunity to enter either a career in science or anything involving numbers.
Examples include Engineering, Astrophysics, Teaching, Banking, Accountancy or Music and Sound Technology.